What is a normal uterus?
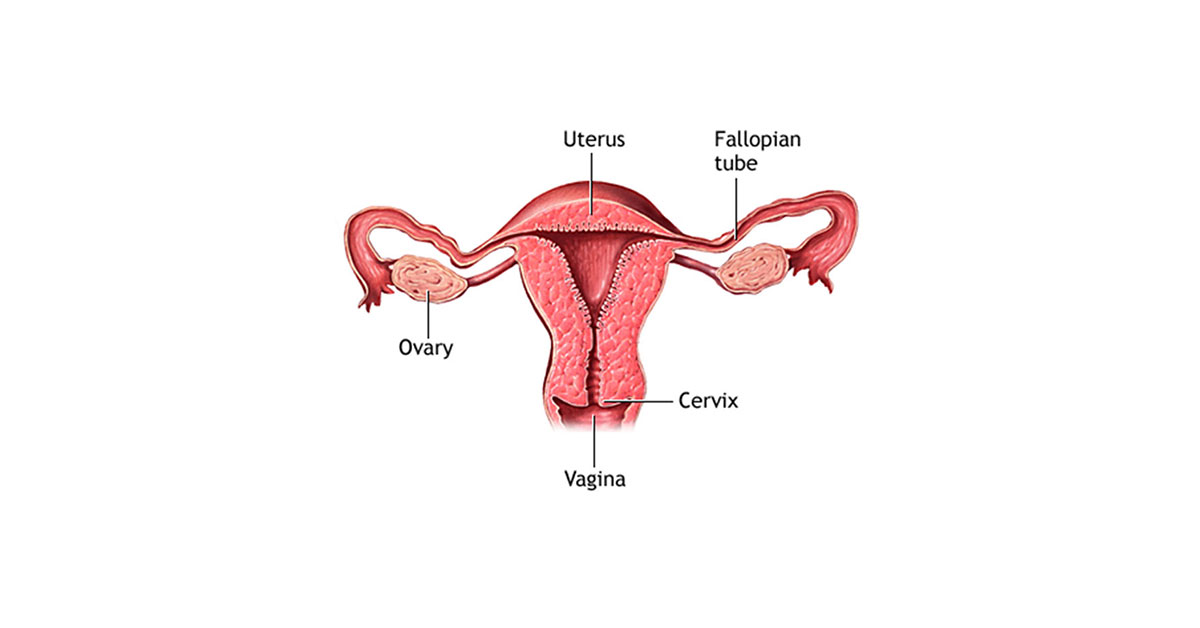
The uterus is an organ shaped like a pear and is located within the female pelvis. It is approximately 7.5 cm long, 5 cm wide and 2.5-3 cm deep. The lower third of the uterus extends into the vagina and is called the cervix (cervix uteri).The upper part is called the fundus(fundus uteri)and is the area where the fertilized embryo nestles and continues with its development into a fetus. The middle part is the largest and is called the body of the uterus (corpus uteri). Both sides of the uterus continue into the fallopian tubes, each connected with one ovary (ovarium)full of eggs.
The uterus lies on the front side next to the bladder. This is a position called anteflexio or anteversio uteri.Some women have their uterus inclined in the other direction, towards the colon, which is a position called retroflexio or retroversio uteri, and is found in 40% of the female population. This condition is not considered as abnormal, it does not affect the chances of conception, or limit the ability of the semen to enter the interior of the uterus, move through the fallopian tubes up to the eggs and inseminate them. The terms refer to the possible position of the uterus in regards to the bladder.
What is an abnormal uterus?
A certain percent of women have a uterus that can be different in its structure (not its position). It is difficult to determine the percentage in the general population, since this condition remains undetected in a certain percent of women. In women that seek help because of difficulties in getting pregnant, the condition in present in 1 of 13 patients. In cases where there is a history of early or late repetitive miscarriages or premature delivery. The percent is much higher – 1 of 3 patients
Can I conceive if I have an abnormal uterus?
Depending on the type of the anomaly. Generally, the anomalies of the uterus do not have to influence the ability to conceive. Once there is a conception, the existence of the abnormality will be visible during the ultrasound. This condition can still be the cause for early or late miscarriage or premature delivery.
What are the abnormalities of the uterus?
- Agenesis(agenesio uteri)– a very rare condition, where the vagina is formed irregularly or has a very short length, and the uterus is very small or does not exist.The condition is revealed when the expected first menstrual cycle does not occur. The only possibility for a woman with agenesis of the uterus to have offspring is through a surrogate mother. The ovaries have a normal build and function.
- Uterus didelphys (uterus didelphus)–condition where the uterus has two cavities. Each cavity extends into a separate cervix and ends into a common vagina (unicollis) or two separate vaginas (bicollis) for each cavity.Each is connected with a fallopian tube and one ovary. This is not a common condition, and a pregnancy with this condition can come to full term. However, this condition can be a cause for premature delivery, malpresentation of the fetus (irregular position of the fetus in the uterus due to the smaller space), an early or late miscarriage, stagnation of the fetal growth and postpartum bleeding. The pregnancy usually ends in caesarian section (in approximately 82% of the cases).
- Unicornuate uterus (uterus unicornis)– condition where there is an agenesis (it does not exist) of one of the horns of the uterus, its size is half the normal size and there is only one fallopian tube. The uterus is shaped like a banana.The reduced horn can have a small cavity with a functional endometrium (in 60% of the cases). This is a very rare anomaly and it occurs at an early age when the tissue that builds the uterus does not develop properly. Both of the ovaries are usually present, but only one of them is connected with a fallopian tube. If the tube is healthy, there is no obstacle in conception. However, because of the size of the uterus, the risk of miscarriage or premature delivery is increased (because of the decreased space inside the uterus).
- Uterus bicornis (uterus bicornis)– condition where the upper part of the uterus (fundus) is indented and has the shape of a heart. The chances of conception are not significantly lowered, but the risk of miscarriage or premature delivery is increased (because of the decreased space inside the uterus).
- Uterine septum(uterus septus)– condition in which the uterine cavity is partitioned by a muscle or tissue called septum. The same can span up to a certain point in the uterus (partially septate uterus) or reach up to the cervix (completely septate uterus). The chances of conception are lower, and the chances of miscarriage or premature delivery are increased in a septate uterus.
- Arcuate uterus (uterus arcuatus)– condition in which the uterus has a slight recess in its upper part (fundus). This condition is very common, and it does not cause problems in conception or during pregnancy.
How are the abnormalities of the uterus revealed?
- Ultrasound with 3D or 4D probe
- HSG- hysterosalpingography
- HSC-hysteroscopy